16 June 2016
16 June 2016
 Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 64 - 25, pp. 5274-5283.
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 64 - 25, pp. 5274-5283.
 João Almeidaa, Marlene Costaa, Sonia Losada-Barreiro*ab, Fátima Paiva-Martinsa, Carlos Bravo-Díazb, Laurence S. Romstedc
João Almeidaa, Marlene Costaa, Sonia Losada-Barreiro*ab, Fátima Paiva-Martinsa, Carlos Bravo-Díazb, Laurence S. Romstedc
 Autor affilations:
Autor affilations:
*Corresponding authors
aREQUIMTE-LAQV, Departamento de Química e Bioquímica, Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade do Porto, 4169-007, Portugal
bDpt. Química Física, Facultad de Química, Universidad de Vigo, Vigo-Pontevedra, Spain
cDepartment of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Piscataway, New Jersey 08854, United States
![]() E-mail: cbravo@uvigo.es
E-mail: cbravo@uvigo.es
Abstract
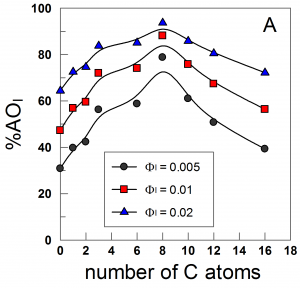
We determined the interfacial molarities of the antioxidants, AOs, hydroxytyrosol (HT), and HT fatty acid esters with chain lengths of 1 to 16 carbons in intact olive oil/water/Tween 20 emulsions. The results were compared with chain length effects on the oxidative stability of the same emulsions, and a direct correlation was established. Both (AOI) molarities (varying 50–250 times greater than the stoichiometric 3.5 × 10–3 M AO concentration) and antioxidant efficiencies show similar parabola-like dependences on AO chain length with a maximum at C8, consistent with the “cut-off” effect often observed at longer chain lengths. Results should aid in understanding the complex structure–reactivity relationships between AO efficiencies in emulsified systems and their hydrophobilic–hydrophobic balance.