Control of antioxidant efficiency of chlorogenates in emulsions: modulation of antioxidant interfacial concentrations. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture
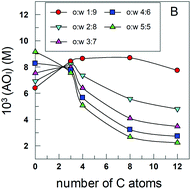
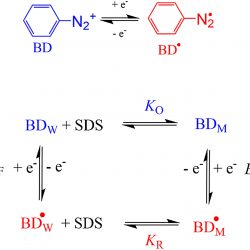
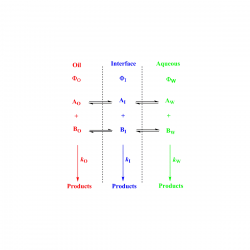
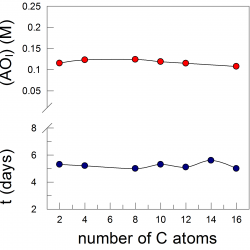
Background Controlling the interfacial concentrations of antioxidants (AOs) in O/W emulsions can be regarded as an unique approach for increasing the efficiency of AOs in inhibiting the oxidation of lipids. Classical methods to determine the AO distribution in binary systems cannot be employed and their distribution needs to be assessed in the intact emulsion [...]