Partitioning and antioxidative effect of protocatechuates in soybean oil emulsions: relevance of emulsifier concentration
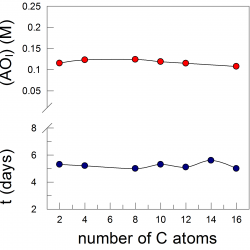
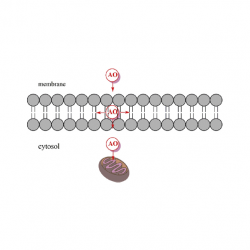
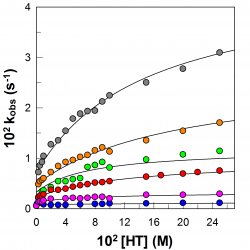
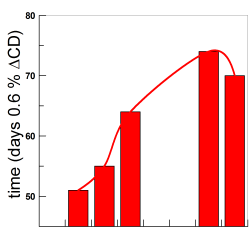
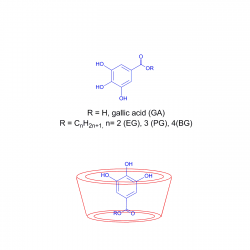
Distributions of a homologous series of protocatechuic acid (PCA) derivatives of increasing lipophilicity were determined in stripped soybean oil-in-water emulsions and compared with their antioxidant (AO) efficiencies. The distribution was determined by employing a recently developed a kinetic method, based on the reaction between the hydrophobic 4-hexadecylbenzenediazonium ions (16-ArN2+) [...]