The location of amphiphobic antioxidants in micellar systems: the diving-swan analogy
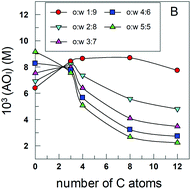
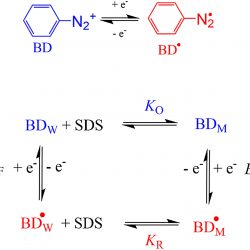
The location of antioxidants (AOs) in a micellar system was determined with the aid of a recently described protocol. The protocol was applied to trolox, caffeic, and gallic acid derivatives of increasing hydrophobicities. The amphiphobic nature of the AOs determined their insertion and orientation in the micellar interface. Their behaviour in a hetero-phasic system was rationalized with a pictorial simile, the “diving-swan” analogy. [...]