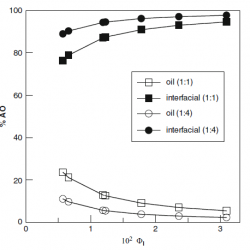
Control of antioxidant efficiency of chlorogenates in emulsions: modulation of antioxidant interfacial concentrations. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture
Background Controlling the interfacial concentrations of antioxidants (AOs) in O/W emulsions can be regarded as an unique approach for increasing the efficiency of AOs in inhibiting the oxidation of lipids. Classical methods to determine the AO distribution in binary systems cannot be employed and their distribution needs to be assessed in the intact emulsion [...]
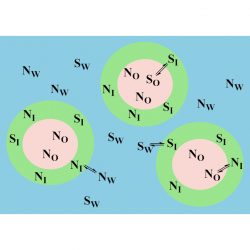
The location of amphiphobic antioxidants in micellar systems: the diving-swan analogy
05 December 2018 Food Chemistry. 1 - 279, pp. 288 - 293. 2018 Sonia Losada-Barreiroc, Amaia Lopez de Arbinaa,b, Marcos Caroli Rezendea, Matias Vidala, Carolina Aliagaa,b* Autor affilations: *Corresponding authors aFacultad de Química y Biología, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Av. B.O’Higgins 3363, Santiago, Chile bCentro para el Desarrollo de la Nanociencia y la Nanotecnología, CEDENNA, Read more about The location of amphiphobic antioxidants in micellar systems: the diving-swan analogy[...] [...]
Differential partitioning of lipophilic bioantioxidants in edible oil-water and octanol-water
Partition coefficients, PWO, of antioxidants (AOs) between edible oils and water are scarce in the literature, despite that AOs are widely used to control lipid oxidation and the oxidative stress in cells. PWO values have a great importance to predict the efficiency and distribution of bioactives at different levels of biological organization from binary oil–water systems to living cells [...]
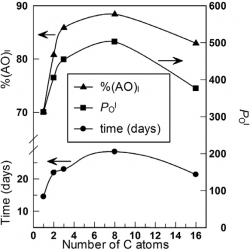
Enhancement of the antioxidant efficiency of gallic acid derivatives in intact fish oil-in-water emulsions throught optimization of their interfacial concentrations
The antioxidant (AO) efficiencies and the distributions of gallic acid (GA) and a series of alkyl gallates (propyl, PG, butyl, BG, octyl, OG and lauryl, LG) were determined in intact fish oil-in-water emulsions. The efficiency of the AOs in inhibiting the oxidation of the fish oil lipids increases upon increasing AO hydrophobicity up to a maximum (∼3-fold) at the octyl derivative, after which the efficiency decreases (LG) [...]
Modulating the interfacial concentration of gallates to improve the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions
The distributions of some gallates were determined in intact fish oil emulsions. % gallates at the interface increases upon increasing surfactant volume fraction ΦI. On the contrary, their interfacial concentrations decrease upon increasing ΦI. Their efficiencies correlate directly with the gallate interfacial concentrations. Butyl and octyl gallates were the most suitable to protect the fish emulsions. [...]
Partitioning of aryl radicals in micellar systems
19 February 2018 Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry. 2018 Sonia Losada-Barreiroa, Andrzej Sienkiewiczb, Carlos Bravo-Díaza Autor affilations: *Corresponding authors aDepartanento de Química Física, Universidad de Vigo, Spain Determining the association constants of radicals to biomimetic systems is not a simple task because of the inherent experimental difficulties associated to their “in‐situ” generation together with their high Read more about Partitioning of aryl radicals in micellar systems[...] [...]
Toxicity of phenolipids: Protocatechuic acid alkyl esters trigger disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase activation in macrophages.
Phenolipids are a class of phenolic compounds with a lipidic moiety that have been receiving increasing attention due to their promising biological activities; however data regarding their toxicity and mechanism of action are scarce. A series of 11 phenolipids consisting of alkyl esters derivatives of the natural molecule protocatechuic acid was synthesized and evaluated against a panel of cancer and non-cancer cell lines [...]
Using pseudophase models to determine antioxidant distributions in emulsions: why dynamic equilibrium matters
Distributions of a homologous series of protocatechuic acid (PCA) derivatives of increasing lipophilicity were determined in stripped soybean oil-in-water emulsions and compared with their antioxidant (AO) efficiencies. The distribution was determined by employing a recently developed a kinetic method, based on the reaction between the hydrophobic 4-hexadecylbenzenediazonium ions (16-ArN2+) and the antioxidants [...]
Partitioning and antioxidative effect of protocatechuates in soybean oil emulsions: relevance of emulsifier concentration
Distributions of a homologous series of protocatechuic acid (PCA) derivatives of increasing lipophilicity were determined in stripped soybean oil-in-water emulsions and compared with their antioxidant (AO) efficiencies. The distribution was determined by employing a recently developed a kinetic method, based on the reaction between the hydrophobic 4-hexadecylbenzenediazonium ions (16-ArN2+) [...]
Free radicals and polyphenols: The redox chemistry of neurodegenerative diseases
The oxidation of bioorganic materials by air and, particularly, the oxidative stress involved in the cell loss and other pathologies associated with neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) are of enormous social and economic importance. NDs generally involve free radical reactions, beginning with the formation of an initiating radical by some redox, thermal or photochemical process [...]
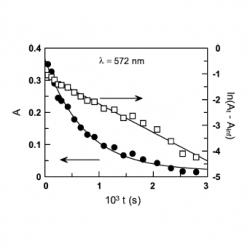
Kinetic evidence for the formation of diazo ethers in the course of reactions between arenediazonium ions and antioxidants
The reactions between arenediazonium ions, ArN2+, and phenolic antioxidants, AOs, are of interest because ArN2+ are involved in carcinogenic and mutagenic processes in contrast to phenolic AOs, that have biological activity and potential beneficial effects on health, and because an ArN2+ is currently being employed as a chemical probe to assess the distribution of AOs in lipid-based food emulsions [...]
Physical evidence that the variations in the efficiency of homologous series of antioxidants in emulsions are due to differences in their partitioning
The relationships between the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of antioxidants (AOs) and their distributions and efficiencies in emulsions are not fully understood. Recent reports indicate that, for series of homologous antioxidants of different hydrophobicity, the variation of their efficiency with the HLB of the AO increases with the alkyl chain length up to a maximum (C3 -C8ester) followed by a decrease [...]
Optimizing the efficiency of antioxidants in emulsions by lipophilization:tuning interfacial concentrations
Optimization of the efficiency of antioxidants, AOs, in lipid-based emulsions via chemical modifications of their reactive moieties is not always possible because of the inherent experimental difficulties and because of the regulatory status of AOs. Esterification of hydrophilic AOs may be a practical, convenient, alternative approach [...]
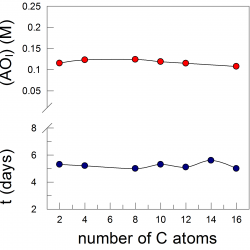
Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol and its Lipophilic Esters in Intact Olive Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Effects of Antioxidant Hydrophobicity, Surfactant Concentration and the Oil to Water Ratio on the Oxidative Stability of the Emulsions
We determined the interfacial molarities of the antioxidants, AOs, hydroxytyrosol (HT), and HT fatty acid esters with chain lengths of 1 to 16 carbons in intact olive oil/water/Tween 20 emulsions. The results were compared with chain length effects on the oxidative stability of the same emulsions, and a direct correlation was established [...]
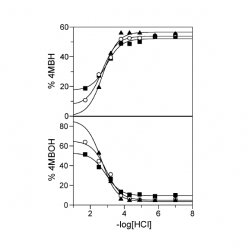
kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between 3-methylbenzenediazonium ions and catechol
We have investigated the kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between 3-methylbenzenediazonium, 3MBD, ions and catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene, [CAT]) in aqueous buffer solution under acidic conditions by employing spectrometric UV/VIS. The variation of the observed rate constant, kobs, with the acidity at a given [CAT] follows an upward curve [...]
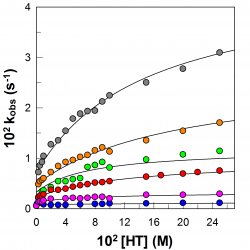
A physicochemical study of the effects of acidity on the distribution and antioxidant efficiency of Trolox in olive-oil in water emulsions
The efficiency of antioxidants to inhibit the oxidation of lipid-based emulsions depends on several factors including their nature and their concentration at the reaction site. Here, we have analyzed the effects of acidity and of surfactant concentration on the distribution and efficiency of the vitamin E analog Trolox (TR) in stripped olive oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with Tween 20 [...]
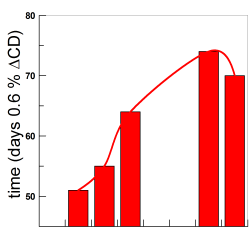
Encapsulation and solubilization of antioxidants gallic acid and ethyl, propyl and butyl gallate with B-cyclodextrin
We investigated the formation of inclusion complexes of the antioxidants (AOs) gallic acid, GA, and its hydrophobic derivatives ethyl (EG), propyl (PG) and butyl (BG) gallate with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) by employing the UV spectral shifts method and, for the sake of comparisons, a modified phase-solubility method that exploits the use of a competitive guest molecule (acetonitrile, ACN) that completely removes the antioxidants from the CD cavity and, at the same time, keeps them in solution [...]
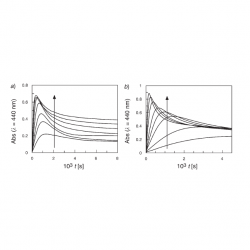
Interfacial kinetics in octane based emulsions. Effects of surfactant concentration on the reaction between 16-ArN2+ and octyl and lauryl gallates
Here we have applied the formalism of the pseudophase kinetic model to analyze the reactivity of 4-hexadecylbenzenediazonium, 16-ArN2+, ions with the antioxidants octyl gallate (OG) and lauryl gallate (LG) in emulsions composed of octane, acidic water and hexaetyleneglycol monododecyl ether, C12E6 [...]
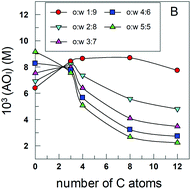
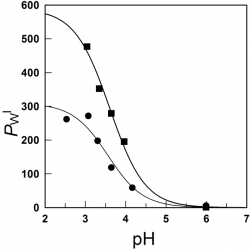
Distributions of phenolic acid antioxidants between the interfacial and aqueous regions of corn oil emulsions: effects of acidity and emulsifier concentration
The oxidative stability of emulsions depends on acidity because pH may affect, among other things, the concentration of antioxidants (AOs) at the reaction site. Here we investigated the effects of pH on the partition constant, PWI, and the distribution of two phenolic acid AOs, gallic (GA) and caffeic (CA), between the aqueous (W) and interfacial (I) regions, in emulsions of 1:9 (vol:vol) corn oil/acidic water [...]
A direct correlation between the antioxidant efficiencies of caffeic acid and its alkyl esters and their concentrations in the interfacial region of olive oil emulsions. The pseudophase model interpretation of the “cut-off” effect
Recently published results for a series of homologous antioxidants, AOs, of increasing alkyl chain length show a maximum in AO efficiency followed by a significant decrease for the more hydrophobic AOs, typically called the "cut-off" effect. Here we demonstrate that in olive oil emulsions both antioxidant efficiencies [...]
To model chemical reactivity in heterogeneous emulsions: think homogeneous microemulsions
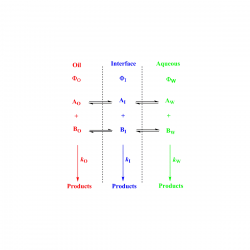
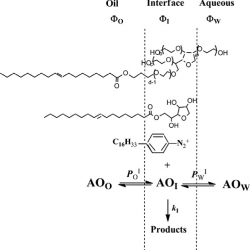
Two important and unsolved problems in the food industry and also fundamental questions in colloid chemistry are how to measure molecular distributions, especially antioxidants (AOs), and how to model chemical reactivity, including AO efficiency in opaque emulsions. The key to understanding reactivity in organized surfactant media is that reaction mechanisms are consistent with a discrete structures–separate continuous regions duality [...]
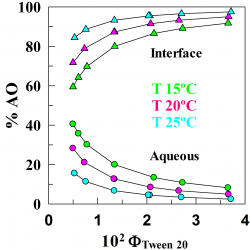
Transfer of antioxidants at the interfaces of model food emulsions: distributions and thermodynamic parameters
Knowledge on the driving force for the hydrophobic effect that partitions antioxidants (AOs) between the oil (O), aqueous (W) and interfacial (I) regions of food emulsions is crucial to predict their efficiency in inhibiting lipid oxidation and to preserve the organoleptic properties of lipid-based foods. Here, we have investigated the effects of temperature [...]
Distribution and antioxidant efficiency of resveratrol in stripped corn oil-in water emulsions
We investigated the effects of resveratrol (RES) on the oxidative stability of emulsions composed of stripped corn oil, acidic water and Tween 20 and determined its distribution in the intact emulsions by employing a well-established kinetic method. The distribution of RES is described by two partition constants, that between the oil-interfacial region, POI, and that between the aqueous and interfacial region, PWI [...]
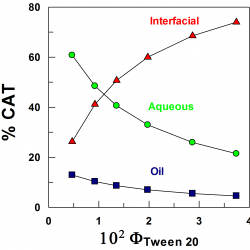
Distribution of catechol in corn oil emulsions
In this work, we have evaluated the effects of emulsifier concentration on the distribution of catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene, CAT) in food-grade emulsions composed of stripped corn oil, acidic water, and Tween 20. Auxiliary experiments in binary stripped corn oil–water mixtures, in the absence of emulsifier, showed that CAT is both oil and water soluble (partition constant math formula = 0.34) [...]
Influence of temperature on the distribution of catechin in corn oil-in water emulsions and some relevant thermodynamic parameters
We investigated the effects of increasing temperature and emulsifier volume fraction (ΦI) on the distribution of catechin (CAT) in stripped corn oil-in-water emulsions. We also estimated relevant thermodynamic parameters for the transfer of CAT from the aqueous to the interfacial region because CAT is sparingly soluble in corn oil and mainly distributes between the aqueous and interfacial regions of emulsions [...]
Effects of acidity, temperature and emulsifier concentration on the distribution of caffeic acid in stripped corn and olive oil in water emulsions
We evaluated the effects of oil type, oil to water ratio, emulsifier concentration, acidity, and temperature on the distribution of caffeic acid, CA, in emulsions composed of stripped olive and corn oils, acidic water, and Tween 20. CA mainly distributes between the water and interfacial regions because it is sparingly soluble in oils, as demonstrated by auxiliary partitioning experiments in the absence of an emulsifier [...]
Maxima in antioxidant distributions and efficiencies with increasing hydrophobicity of gallic acid and its alkyl esters. The pseudophase model interpretation of the “cutoff effect”
Antioxidant (AO) efficiencies are reported to go through maxima with increasing chain length (hydrophobicity) in emulsions. The so-called “cutoff” after the maxima, indicating a decrease in efficiency, remains unexplained. This paper shows, for gallic acid (GA) and propyl, octyl, and lauryl gallates (PG, OG, and LG, respectively) [...]
Effects of emulsifier hydrophile-lipophile balance and emulsifier concentration on the distributions of gallic acid, propyl gallate, and α-tocopherol in corn oil emulsions
We evaluated the effects of the hydrophile-lipophile balance (HLB) and emulsifier concentration on the distribution of the antioxidants gallic acid (GA), propyl gallate (PG), and α-tocopherol (TOC) between the aqueous, interfacial, and oil regions of food-grade emulsions composed of stripped corn oil, acidic water, and a mixture of the non-ionic surfactants Tween 20, 40, 80, and Span 20 [...]
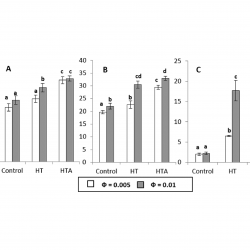
Distribution of Hydroxytyrosol and Hydroxytyrosol Acetate in Olive Oil Emulsions and Their Antioxidant Efficiency
We employed a kinetic method to determine the distributions of the antioxidants hydroxytyrosol (HT) and hydroxytyrosol acetate (HTA) between the oil, aqueous, and interfacial regions of a model food emulsion composed of stripped olive oil, acidic water, and a blend of Tween 80 and Span 80 [hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) = 8.05] as an emulsifier [...]
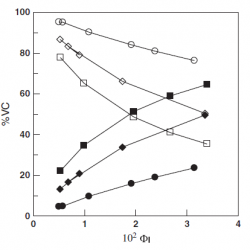
Effects of acidity and emulsifier concentration on the distribution of Vitamin C in a model food emulsion
We have analyzed the effects of acidity and emulsifier concentration on the distribution of ascorbic acid or vitamin C (VC) in a model emulsion prepared by mixing octane, acidic (HCl) water and the non-ionic surfactant hexaethyleneglycol monododecyl ether (C12E6). VC is oil insoluble, and only the partition constant between the interfacial and aqueous regions (PWI) is needed to describe its distribution within the emulsion [...]
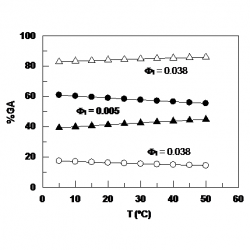
Temperature and emulsifier concentration effects on gallic acid distribution in a model food emulsion
We determined the effects of emulsifier concentration and temperature on the distribution of gallic acid (GA) in a food-grade emulsion composed of 1:9 vol:vol stripped corn oil, acidic water and Tween 20. The distribution of GA can be defined by the partition constant between the aqueous and the interfacial regions, View the MathML source, which was determined by using a kinetic method and the pseudophase kinetic model [...]
Distribution of Tert-Butylhydroquinone in a Corn Oil/C12E6/Water Based Emulsion. Application of the Pseudophase Kinetic Model
We have determined the distribution of the antioxidant tert-butylhydroquinone, TBHQ, between the oil and interfacial regions of an emulsion composed of stripped corn oil, acidic water and hexaethyleneglycol monododecyl ether, C12E6, by employing a kinetic method based on the reaction between the hydrophobic 16-hexadecylbenzenediazonium ions, 16-ArN2+, and TBHQ [...]
Butanolysis of 4-methylbenzenediazonium ions in binary n-BuOH/H2O mixtures and in n-BuOH/SDS/H2O reverse micelles. Effects of solvent composition, acidity and temperature on the switch between heterolytic and homolytic dediazoniation mechanisms
We investigated the effects of solvent composition, acidity and temperature on the switch between heterolytic and homolytic mechanisms in the course [...]
Reactivity of 3-Methylbenzenediazonium ions with Gallic Acid. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Reaction
We investigated the kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between the 3-methylbenzenediazonium ions (3MBD), and gallic acids (=3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid; GA) in aqueous buffer solution under acidic conditions by employing spectrometric, electrochemical, and chromatographic techniques and computational methods [...]
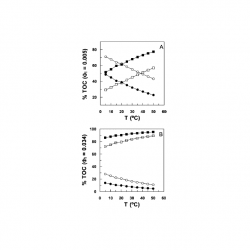
Effects of Temperature and Emulsifier Concentration on α-Tocopherol Distribution in a Stirred, Fluid, Emulsion. Thermodynamics of α-Tocopherol Transfer between the Oil and Interfacial Regions
The combined linear sweep voltammetry (LSV)/pseudophase kinetic model method was used to obtain the first estimates of the free energies, enthalpy, and entropies of transfer of α-tocopherol (TOC) between the oil and interfacial regions of fluid, opaque, emulsions of n-octane [...]
Dediazoniation of 1-naphthalenediazonium tetrafluoroborate in aqueous acid and in micellar solutions
We have measured the rates and product yields of dediazoniation of 1-naphthalenediazonium (1ND) tetrafluoroborate in the presence and absence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micellar aggregates by employing a combination of UV–vis spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography [...]
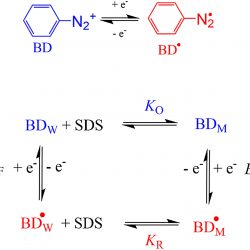
Micellar effects on the reaction between an arenediazonium ion and the antioxidants gallic acid and octyl gallate
The effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelles on the reaction between the 3-methylbenzenediazonium (3MBD) ion and either the hydrophilic antioxidant gallic acid (GA) or the hydrophobic analogue octyl gallate (OG) have been investigated as a function of pH [...]
Kinetic and Mechanism of the reaction between 4-hexadecylbenzenediazonium ions and vitamin C in emulsions: Further evidence of the formation of diazo ether intermediates in the course of the reaction
The kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between hydrophobic 4-hexadecylarenediazonium ions, 16-ArNmath image and vitamin C, VC, in a model emulsion prepared by mixing octane, acidic (HCl) water and the non-ionic surfactant hexaethyleneglycol monododecyl ether, C12E6, were investigated [...]
Quantitative determination of alpha-tocopherol distribution in a tributyrin/Brij 30/water model food emulsion
Until recently, determining the distribution of antioxidants, AOs, between the oil, interfacial and aqueous regions of opaque emulsions has not worked well because the concentrations of AOs in interfacial regions cannot be determined separately from their concentrations in the oil and water phases [...]
Kinetics and Mechanism of the Reaction between an Arenediazonium Ion and Methyl Gallate (=Methyl 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoate) in Aqueous Solution: Evidence for Diazo Ether Formation through an O-Coupling Reaction
We have investigated the kinetics and mechanism of the reaction between 3-methylbenzenediazonium ions (3MBD) and methyl gallate (=methyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate; MG), in aqueous buffer solution by employing spectrophotometric (UV/VIS) and electrochemical (linear-sweep voltammetry, LSV) techniques [...]