Modulating the interfacial concentration of gallates to improve the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions
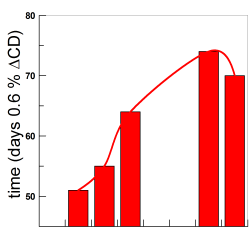
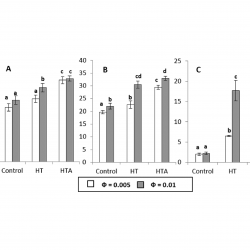
The distributions of some gallates were determined in intact fish oil emulsions. % gallates at the interface increases upon increasing surfactant volume fraction ΦI. On the contrary, their interfacial concentrations decrease upon increasing ΦI. Their efficiencies correlate directly with the gallate interfacial concentrations. Butyl and octyl gallates were the most suitable to protect the fish emulsions. [...]