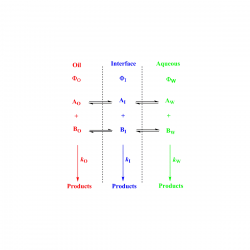
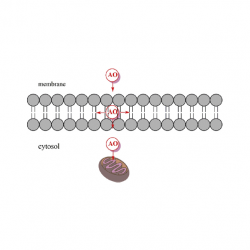
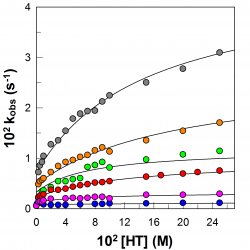
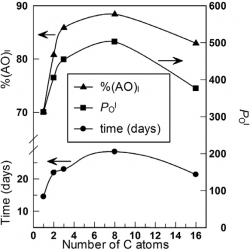
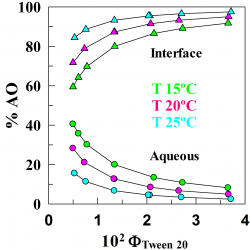
The location of amphiphobic antioxidants in micellar systems: the diving-swan analogy
05 December 2018 Food Chemistry. 1 - 279, pp. 288 - 293. 2018 Sonia Losada-Barreiroc, Amaia Lopez de Arbinaa,b, Marcos Caroli Rezendea, Matias Vidala, Carolina Aliagaa,b* Autor affilations: *Corresponding authors aFacultad de Química y Biología, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Av. B.O’Higgins 3363, Santiago, Chile bCentro para el Desarrollo de la Nanociencia y la Nanotecnología, CEDENNA, Read more about The location of amphiphobic antioxidants in micellar systems: the diving-swan analogy[...] [...]